高级操作
Setup
使用 Playbooks 时,Ansible 会自动执行 setup module 以收集各个 Managed node 的 facts。从 IP 位址、作业系统、CPU 等资讯应有尽有。
ansible -i hosts all -m setup > setup.txt
Template 系统
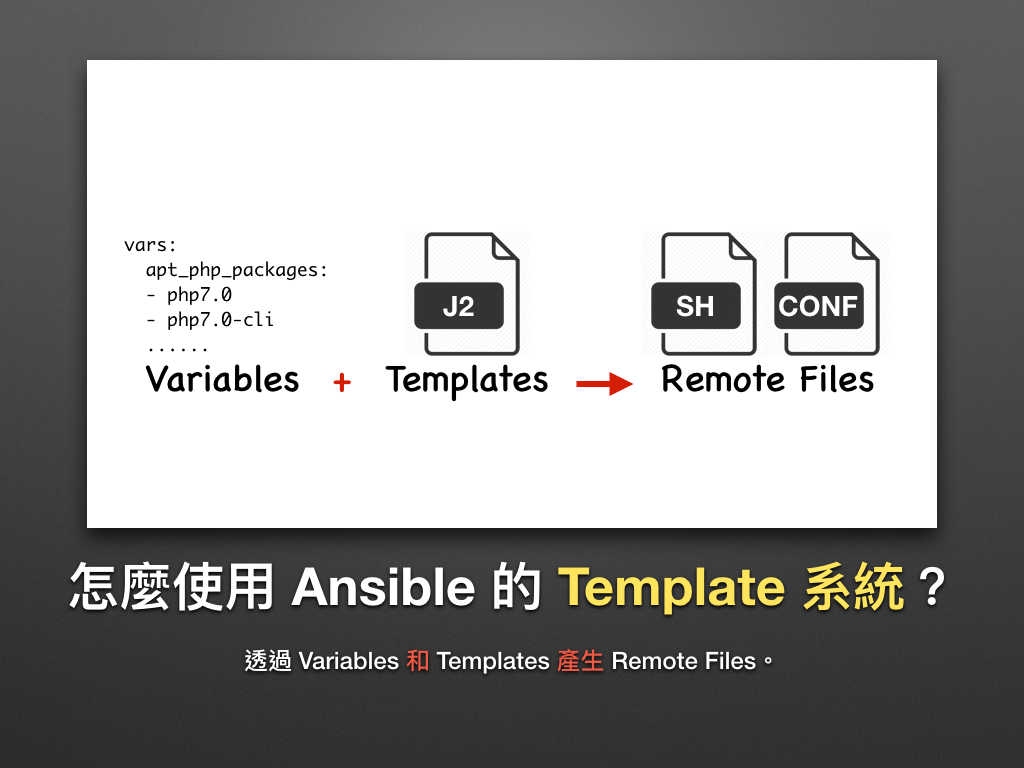
我们只需事先定义变数和模板 (Templates),即可用它动态产生远端的 Shell Scripts、设定档 (Configure) 等。换句话说,我们可以用一份 template 来产生开发 (Development)、测试 (Test) 和正式环境 (Production) 等不同的环境设定。
举例说明
- 准备文件。
vi hello_world.txt.j2
Hello "{{ dynamic_word }}" ↑ ↑ ↑
由于 Ansible 是借由 Jinja2 来写作 template 系统,所以请使用 *.j2 的副档名。
上面的"{{ dynamic_word }}"代表我们在此 template 里使用了名为 dynamic_word 的变数。
- 建立 playbook,并加入变数。
vi template_demo.yml
---
- name: Play the template module
hosts: all
vars:
dynamic_word: "World"
tasks:
- name: generation the hello_world.txt file
template:
src: hello_world.txt.j2
dest: /tmp/hello_world.txt
- name: show file context
command: cat /tmp/hello_world.txt
register: result
- name: print stdout
debug:
msg: "{{ result.stdout }}"
- dynamic_word 变数设了一个预设值 World。
- 使用了 template module,并指定了档案的来源 (src) 和目的地 (dest)。
- 之后的 2 个 tasks 则是把 template module 产生出来的档案给印出来。
- 执行 playbook。
ansible-playbook -i hosts template_demo.yml
执行完以后所有的机器都生成了/tmp/hello_world.txt文件。并且内容为Hello "World" ↑ ↑ ↑。
通过 -e 参数将 dynamic_word 覆写成 Day50。
ansible-playbook -i hosts template_demo.yml -e "dynamic_word=Day50"
[root@h6 ~]# cat /tmp/hello_world.txt
Hello "Day50" ↑ ↑ ↑
怎么让 Playbooks 切换不同的环境?
- 在 Playbooks 里除了用 vars 来宣告变数以外,还可以用 vars_files 来 include 其它的变数档案。
---
- name: Play the template module
hosts: all
vars:
dynamic_word: "World"
vars_files:
- vars/test.yml
- vars/development.yml
tasks:
- name: generation the hello_world.txt file
template:
src: hello_world.txt.j2
dest: /tmp/hello_world.txt
- name: show file context
command: cat /tmp/hello_world.txt
register: result
- name: print stdout
debug:
msg: "{{ result.stdout }}"
- 建立 vars/development.yml, vars/test.yml 和 vars/production.yml 档案,接下来将依不同的环境 include 不同的变数档案 (vars files),这样就可以用同一份 playbook 切换环境了!
Development
mkdir vars
cd vars
vi development.yml
dynamic_word: "development"
Test
mkdir vars
cd vars
vi test.yml
dynamic_word: "test"
- 执行playbook,并通过 -e 切换各个环境。
vars_files:
- vars/test.yml
- vars/development.yml
要执行那个就保留那个文件,比如就是要test里面的变量那么就
vars_files:
- vars/test.yml
要执行那个就保留那个文件,比如就是要development里面的变量那么就
vars_files:
- vars/development.yml
ansible-playbook -i hosts template_demo.yml
ansible-playbook -i hosts template_demo.yml
Handlers
Handler 本身是一种非同步的 callback function ;在这里则是指关连于特定 tasks 的事件 (event) 触发机制。当这些特定的 tasks 状态为被改变 (changed) 且都已被执行时,才会触发一次 event。
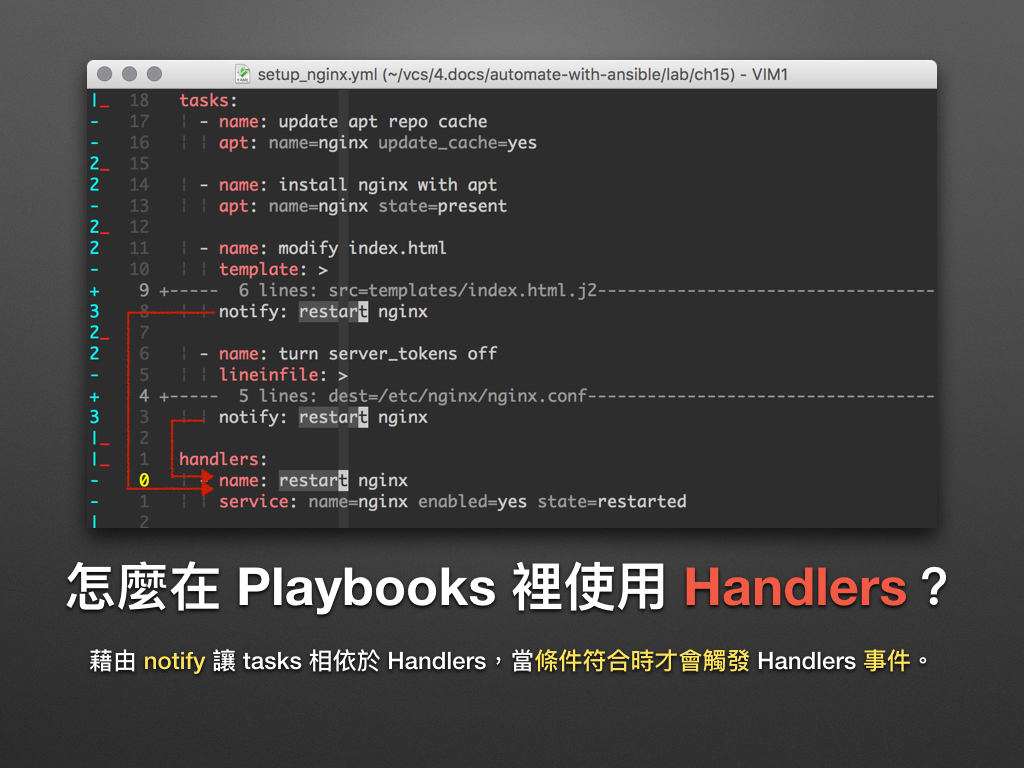
以上图为例,要触发 restart nginx 这个 handler,需符合以下条件:
- modify index.html 或 turn server_tokens off 两个 tasks 中,至少有一个状态为 changed。
- 所有关连到 restart nginx handler 的 tasks 都已被执行。
基本使用
---
- name: setup the nginx
hosts: all
become: true
vars:
username: "ironman"
mail: "chusiang (at) drx.tw"
blog: "http://note.drx.tw"
tasks:
# 执行 'apt-get update' 指令。
- name: update apt repo cache
apt: name=nginx update_cache=yes
# 执行 'apt-get install nginx' 指令。
- name: install nginx with apt
apt: name=nginx state=present
# 于网页根目录 (DocumentRoot) 编辑 index.html。
- name: modify index.html
template: >
src=templates/index.html.j2
dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
owner=www-data
group=www-data
mode="644"
backup=yes
notify: restart nginx
# (security) 关闭 server_tokens:移除 server_tokens 前的 '#' 字元。
- name: turn server_tokens off
lineinfile: >
dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
regexp="server_tokens off;"
insertafter="# server_tokens off;"
line="server_tokens off;"
state=present
notify: restart nginx
# handlers
#
# * 当确认事件有被触发才会动作。
# * 一个 handler 可被多个 task 通知 (notify),并于 tasks 跑完才会执行。
handlers:
# 执行 'sudo service nginx restart' 指令。
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx enabled=yes state=restarted
# post_tasks:
#
# 在 tasks 之后执行的 tasks。
post_tasks:
# 检查网页内容。
- name: review http state
command: "curl -s http://localhost"
register: web_context
# 印出检查结果。
- name: print http state
debug: msg=